Telco 5G Development
State of the 5G development.
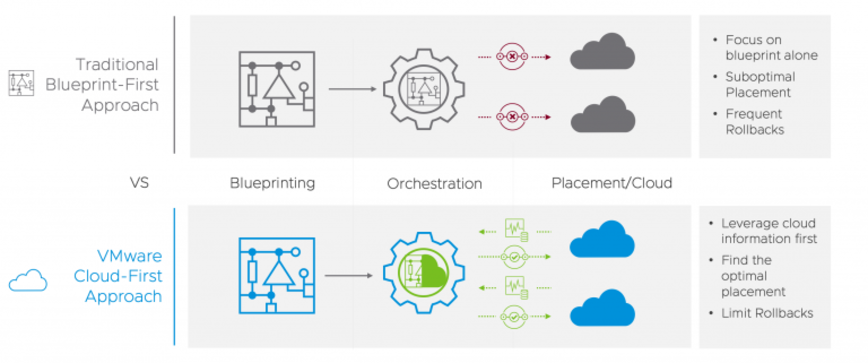
VMware Cloud First Approach. Source: VMware.

VMware Telco Cloud Automation Components. Source: VMware.
Telco 5G Learning Resources
Learning resources by hardware and software providers for the 5G
HPE(Hewlett Packard Enterprise) Telco Blueprints overview
Network Functions Virtualization Infrastructure (NFVI) by Cisco
Introduction to vCloud NFV Telco Edge from VMware
VMware Telco Cloud Automation(TCA) Architecture Overview
Maturing OpenStack Together To Solve Telco Needs from Red Hat
Red Hat telco ecosystem program
OpenStack for Telcos by Canonical
Open source NFV platform for 5G from Ubuntu
Understanding 5G Technology from Verizon
Verizon and Unity partner to enable 5G & MEC gaming and enterprise applications
Understanding 5G Technology from Intel
Understanding 5G Technology from Qualcomm
Telco Acceleration with Xilinx
Amazon EC2 Overview and Networking Introduction for Telecom Companies
Citrix Certified Associate – Networking(CCA-N)
Citrix Certified Professional – Virtualization(CCP-V)
Certified Information Security Manager(CISM)
Wireshark Certified Network Analyst (WCNA)
Juniper Networks Certification Program Enterprise (JNCP)
Cloud Native Computing Foundation Training and Certification Program
Telco 5G Tools and Frameworks
Applications and framework for the 5G implementation, testing and deployment
Open Stack is an open source cloud platform, deployed as infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) to orchestrate data center operations on bare metal, private cloud hardware, public cloud resources, or both (hybrid/multi-cloud architecture). OpenStack includes advance use of virtualization & SDN for network traffic optimization to handle the core cloud-computing services of compute, networking, storage, identity, and image services.
StarlingX is a complete cloud infrastructure software stack for the edge used by the most demanding applications in industrial IOT, telecom, video delivery and other ultra-low latency use cases.
Airship is a collection of open source tools for automating cloud provisioning and management. Airship provides a declarative framework for defining and managing the life cycle of open infrastructure tools and the underlying hardware.
Network functions virtualization (NFV) is the replacement of network appliance hardware with virtual machines. The virtual machines use a hypervisor to run networking software and processes such as routing and load balancing. NFV allows for the separation of communication services from dedicated hardware, such as routers and firewalls. This separation means network operations can provide new services dynamically and without installing new hardware. Deploying network components with network functions virtualization only takes hours compared to months like with traditional networking solutions.
Software Defined Networking (SDN) is an approach to networking that uses software-based controllers or application programming interfaces (APIs) to communicate with underlying hardware infrastructure and direct traffic on a network. This model differs from that of traditional networks, which use dedicated hardware devices (routers and switches) to control network traffic.
Virtualized Infrastructure Manager (VIM) is a service delivery and reduce costs with high performance lifecycle management Manage the full lifecycle of the software and hardware comprising your NFV infrastructure (NFVI), and maintaining a live inventory and allocation plan of both physical and virtual resources.
Management and Orchestration(MANO) is an ETSI-hosted initiative to develop an Open Source NFV Management and Orchestration (MANO) software stack aligned with ETSI NFV. Two of the key components of the ETSI NFV architectural framework are the NFV Orchestrator and VNF Manager, known as NFV MANO.
Magma is an open source software platform that gives network operators an open, flexible and extendable mobile core network solution. Their mission is to connect the world to a faster network by enabling service providers to build cost-effective and extensible carrier-grade networks. Magma is 3GPP generation (2G, 3G, 4G or upcoming 5G networks) and access network agnostic (cellular or WiFi). It can flexibly support a radio access network with minimal development and deployment effort.
OpenRAN is an intelligent Radio Access Network(RAN) integrated on general purpose platforms with open interface between software defined functions. Open RANecosystem enables enormous flexibility and interoperability with a complete openess to multi-vendor deployments.
Open vSwitch(OVS)is an open source production quality, multilayer virtual switch licensed under the open source Apache 2.0 license. It is designed to enable massive network automation through programmatic extension, while still supporting standard management interfaces and protocols (NetFlow, sFlow, IPFIX, RSPAN, CLI, LACP, 802.1ag).
Edge is a distributed computing framework that brings enterprise applications closer to data sources such as IoT devices or local edge servers. This proximity to data at its source can deliver strong business benefits, including faster insights, improved response times and better bandwidth availability.
Multi-access edge computing (MEC) is an Industry Specification Group (ISG) within ETSI to create a standardized, open environment which will allow the efficient and seamless integration of applications from vendors, service providers, and third-parties across multi-vendor Multi-access Edge Computing platforms.
Virtualized network functions(VNFs) is a software application used in a Network Functions Virtualization (NFV) implementation that has well defined interfaces, and provides one or more component networking functions in a defined way. For example, a security VNF provides Network Address Translation (NAT) and firewall component functions.
Cloud-Native Network Functions(CNF) is a network function designed and implemented to run inside containers. CNFs inherit all the cloud native architectural and operational principles including Kubernetes(K8s) lifecycle management, agility, resilience, and observability.
Physical Network Function(PNF) is a physical network node which has not undergone virtualization. Both PNFs and VNFs (Virtualized Network Functions) can be used to form an overall Network Service.
Network functions virtualization infrastructure(NFVI) is the foundation of the overall NFV architecture. It provides the physical compute, storage, and networking hardware that hosts the VNFs. Each NFVI block can be thought of as an NFVI node and many nodes can be deployed and controlled geographically.

